RE Reaches 26% of China’s Electricity Generation in 2017
Based on data from China Electricity Council (CEC) and China’s National Energy Administration (NEA), renewable energy (RE) increased to 26.5% of China’s electricity generation in 2017, while fossils share kept decreasing to 69.7%, and nuclear share accounted for 3.9%.
China Electricity Generation Mix 2010-2017
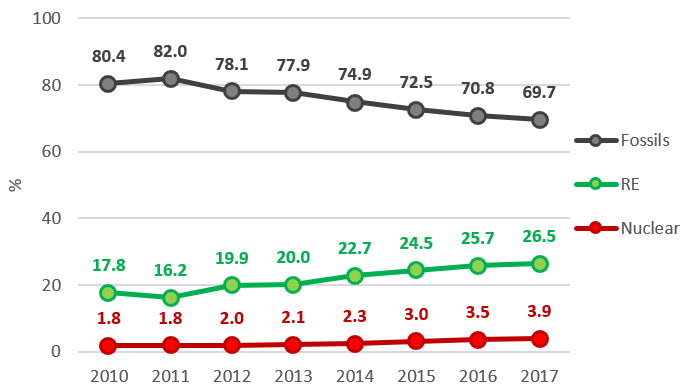
- Notes:Electricity generated from bio has been subtracted from electricity generated from “Fossils.” “Fossils” include coal, gas, oil and other non-renewable waste.
- Sources:China Electricity Council, and China’s National Energy Administration.
The breakdown of this 26.5% RE share is as follows; hydro 18.6%, wind 4.8%, solar 1.8%, and bio 1.2%.
In spite of the fact that the country’s total electricity generation increased by 52% (+2,190 terawatt-hours) between 2010 and 2017, the share of RE increased by 8.7 percentage points, whereas that of fossils decreased by 10.8 percentage points.
The main driver behind RE share growth is wind power, which share in electricity generation increased from 1.2% in 2010 to 4.8% in 2017.






