Wind and Solar Account for Most of New Electricity Generation in Major Economies
Based on data collected from China Electricity Council (CEC) & National Energy Administration (NEA), India Central Electricity Authority (CEA), and the International Energy Agency (IEA) for OECD countries, altogether accounting for roughly 75% of the world’s electricity generation, the majority of new electricity in 2017 came from renewable energy (RE), essentially wind and solar; 281 terawatt-hours (TWh) out of 533 TWh, or 53%. And that despite significant growth in electricity consumption, particularly in China.
Worldwide Change in Electricity Generation (2017-2016)
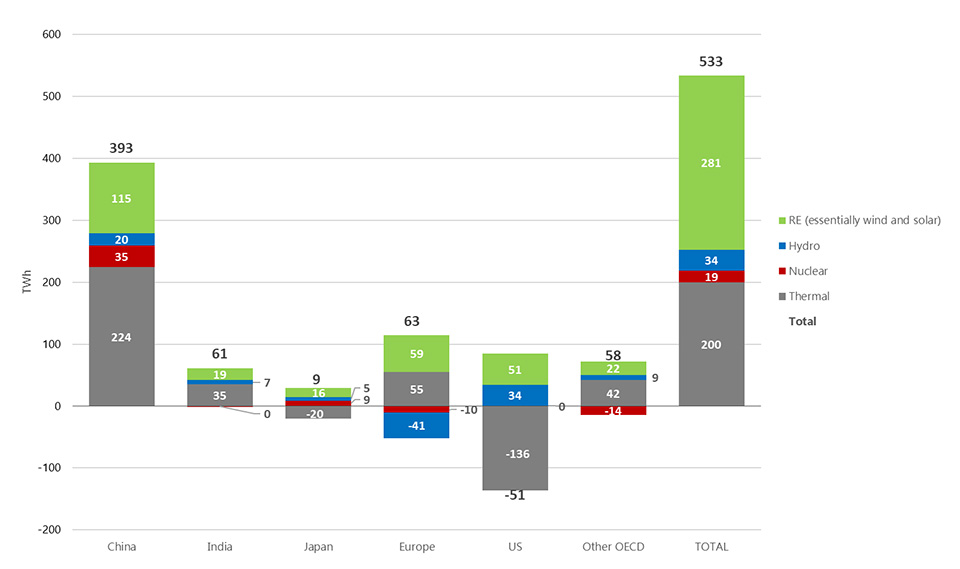
- Notes: "Thermal" includes fossils (coal, oil, and gas) and bio & waste. "Hydro" includes pumped storage. And "RE" includes wind, solar, geo, marine, and other non-combustible sources. “Other OECD” does not include Israel.
- Sources: CEC&NEA (China), CEA (India), and IEA (Others).
And that is China which has contributed the most to the RE growth (+115 TWh), followed by Europe (+59 TWh) and the US (+51 TWh). India (+19 TWh) and Japan (+16 TWh) also played a role.
Fossil fuel electricity generation increased as well (+200 TWh) – but not everywhere. On the one hand it increased in China (+224 TWh) and India (+35 TWh), and also in Europe (+55 TWh), where hydro conditions were exceptionally adverse and French nuclear power struggles continued. On the other hand, it decreased in the US (-136 TWh), regardless of President Trump’s pro-fossil fuel energy policy, and in Japan (-20 TWh).
Finally, growth in electricity generation from nuclear was marginal once again.
At the global scale, data from the IEA indicate that renewables (including hydro and bio) accounted for about half of the world’s new electricity generation in 2017.






